Educational Theories
Behaviourism, Cognitive Psychology, Social Constructivism, Humanism and Connectivisim
Educational theories have always played an essential role in educational practice and research, but which approach matches or reflects our class practice is another story altogether. The academic study of education has evolved uniquely across different geographical, linguistic, intellectual, national and political contexts, leaving room for discourse and individualized adaptations. This section will introduce, explain and demonstrated how educational theories work and how we can recognize them in our practice.

Behaviourism
-
The behaviourist movement has a vast history and has impacted multiple areas of human life and endeavour.
-
Behavioursim, in terms of learning, argues that it is through the altering of behaviour and ensuring the learners' preparedness for learning that the best outcomes will be achieved.
-
In behaviourism, the learner is characterised as being reactive to conditions in the environment as opposed to taking an active role in discovering the environment.The most critical factor, however, is the arrangement of stimuli and consequences within the environment, with the focus being shifted towards the factors that influence learning.
-
Behaviourism promotes a pedagogy based on accuracy, rigour, evaluations, measurements and potential outcomes.
-
It is a pragmatic and practical philosophy rooted in observation and experiment.
Here is some research on behaviourism to help you get a better view of the theory:
Social Constructivism
In social constructivism, the teachers are challenged to look into how they promote the construction of knowledge and stay away away from passive intake of information during lessons.
It's challenging teachers and students to reflect upon their daily experiences and their transfer into own representations and
pre-existing knowledge.
In Social constructivism, individuals build on personal experiences becoming active and social in the process.
The methodology for social constructivism focuses on:
-
Collaboration
-
Scaffolding
-
Self-initiated/ guided learning
-
Peer review and assessment
Here are a series of research paper to help you get a better understanding of social constructivism:
Connectivism
Connectivism explores learning in a digital age; being a relatively new theory, it leaves room for discourse regarding its validation in the educational setting. Connectivism suggests that students have the potential to integrate thoughts, views and general information productively.
Connectivism tries to showcase the importance of technology and its significant influence on the learning process and choice making.
How is it used in the classroom:
-
collaborations
-
discussions
-
discourse
-
problem-solving
-
decision-making
-
rationalisation
Here are some more insights into Connectivism"
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology and education have pursued parallel rather than overlapping directions. Both areas of research have significantly similar ground, since both focus on learning and memory.
In cognitive psychology as in education, the focus is shifted towards the following areas:
-
The organisation of long-term memory
-
Decision making process
-
Concept formation
-
Influence on storage and retrieval from memory
-
Problem solving and transfer.
It is rather common to see practitioners apply strategies in their teaching that no longer accommodate the environmental changes that directly impact the learning, focusing on mass teaching rather than interleaving when explaining topics. Numerous psychologists as well as educationalists have looked into strategies that promote retention and learning in the classroom setting.
Here are some valuable research papers that will give you an extensive look into the areas of study:
Humanism
Humanism is another educational theory that believes in teaching the "whole" child.
Humanism has a strong focus on:
-
emotional development
-
values
-
dignity
-
problem solving through reasoning and science
-
wellbeing
-
personal grown
-
civic responsibility
In humanism, schools always look seek freedom from the pressure of conformity.
There are 3 main beliefs in humanism:
-
human reason
-
human experience
-
reliable knowledge
Here is some more research on humanism to help you get a better picture of the theory:
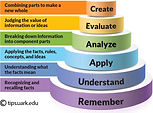
Bloom's Taxonomy
There is no surprise that Bloom's Taxonomy of Educational
Objectives for the cognitive domain have had a massive impact on educational thought and practice worldwide.
Many authors have cited and made various claims about its properties that concern both educational and psychological issues.
Educational issues involve things such as " the facilitation of communication while psychological problems are the categorisations of factors to be "consistent with relevant and accepted psychological principles and theories".
The taxonomy is entering its twenty-second year of existence, a time in which it has been challenged and scrutinised over its validity.
A complete validation of the taxonomy must be regarded through two different stages:
-
Educational properties
-
Psychological properties
Here are some research papers that will support you in your understanding of Bloom's Taxonomy: